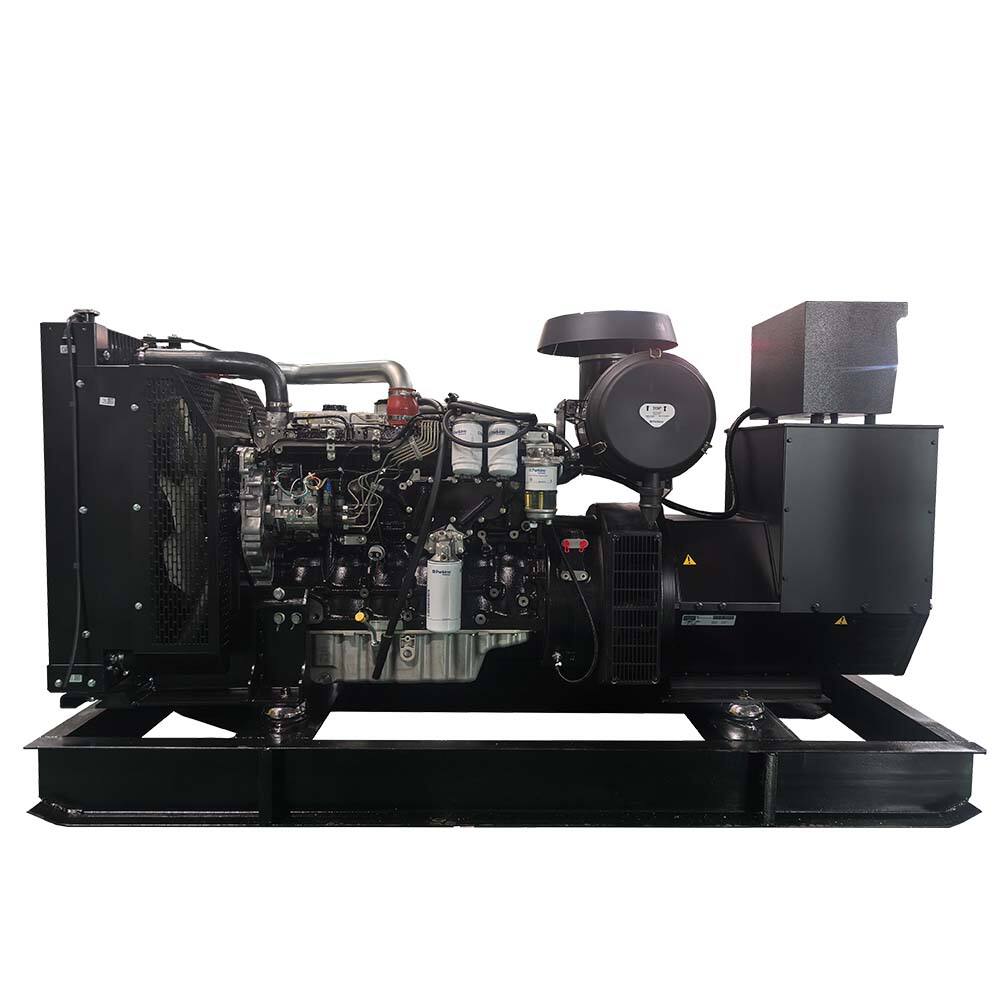
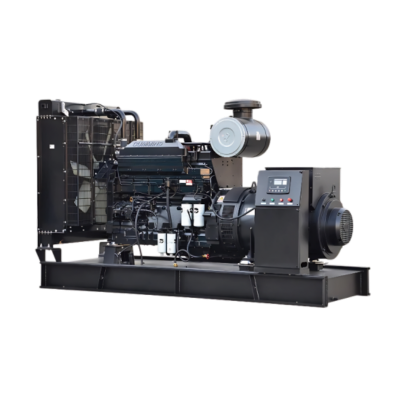
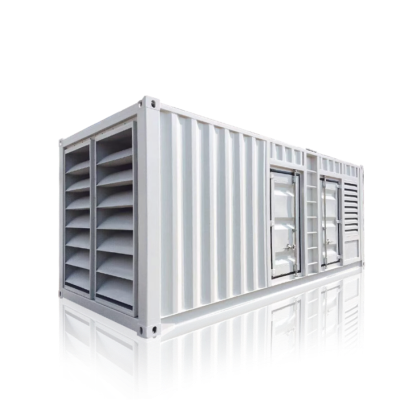
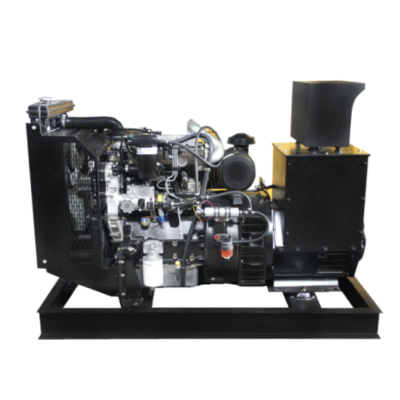
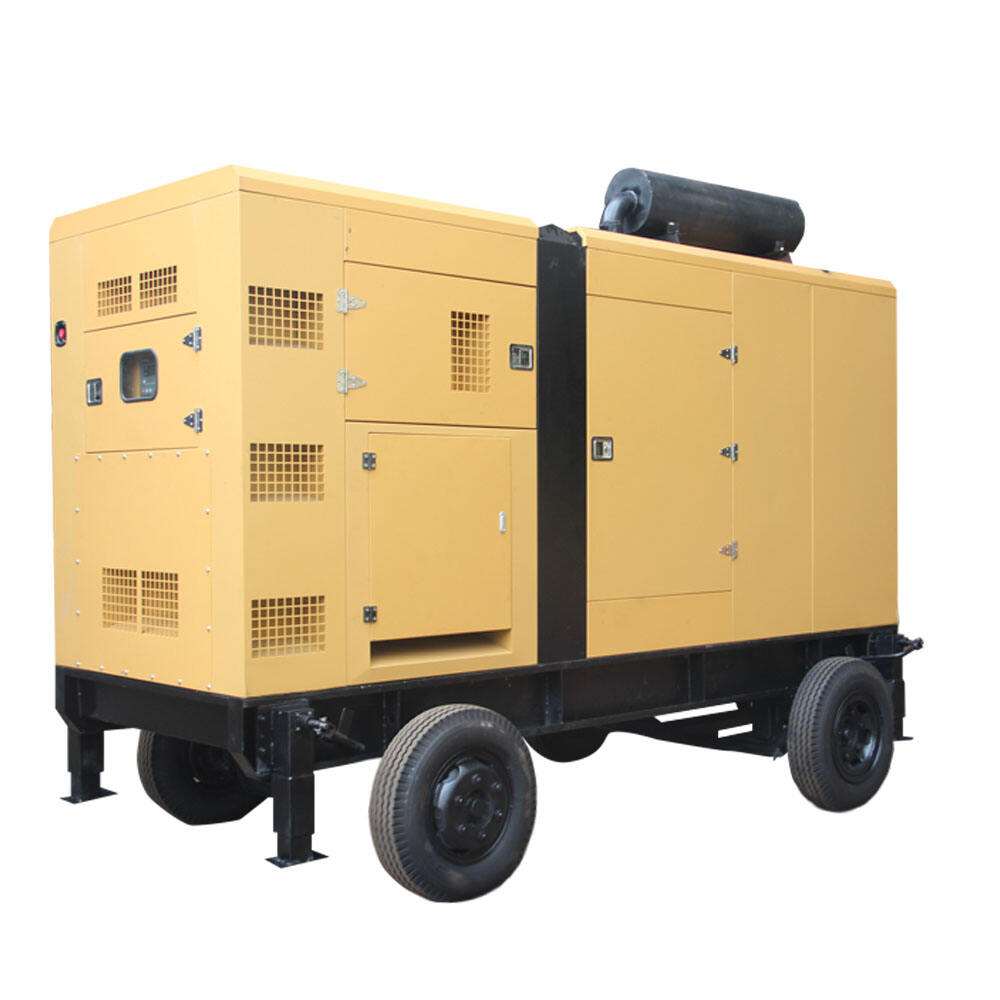
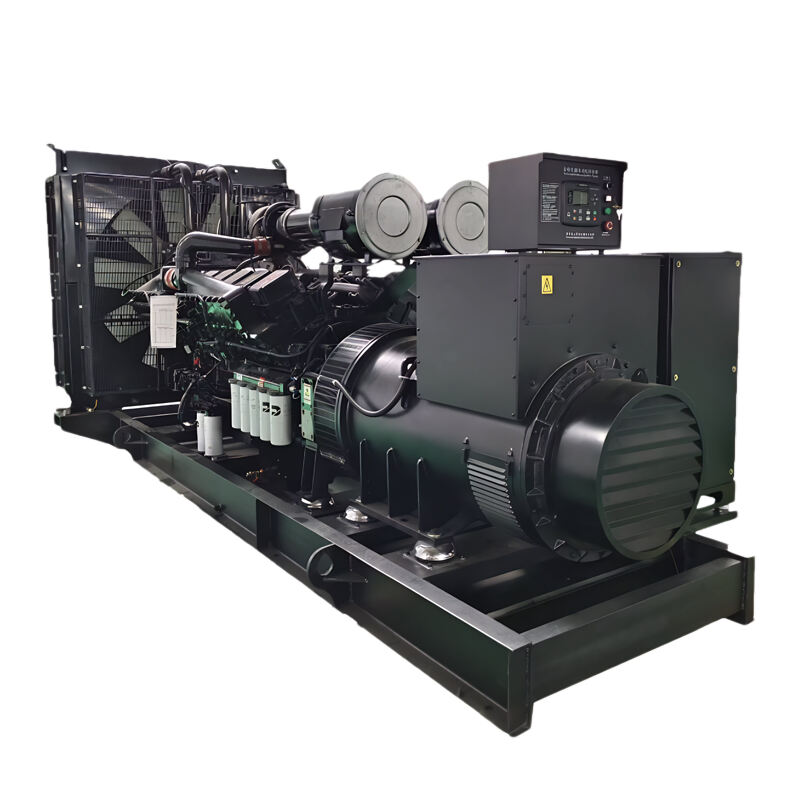
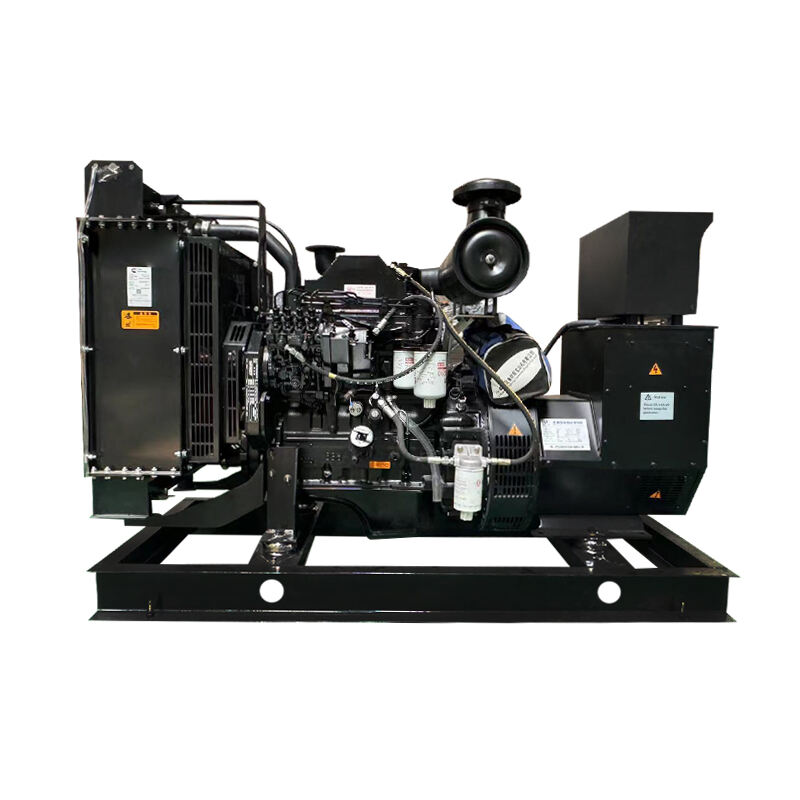
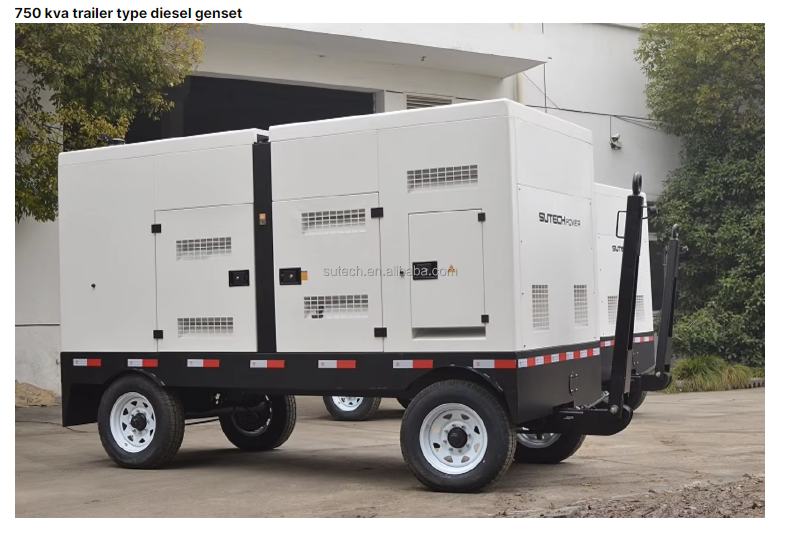
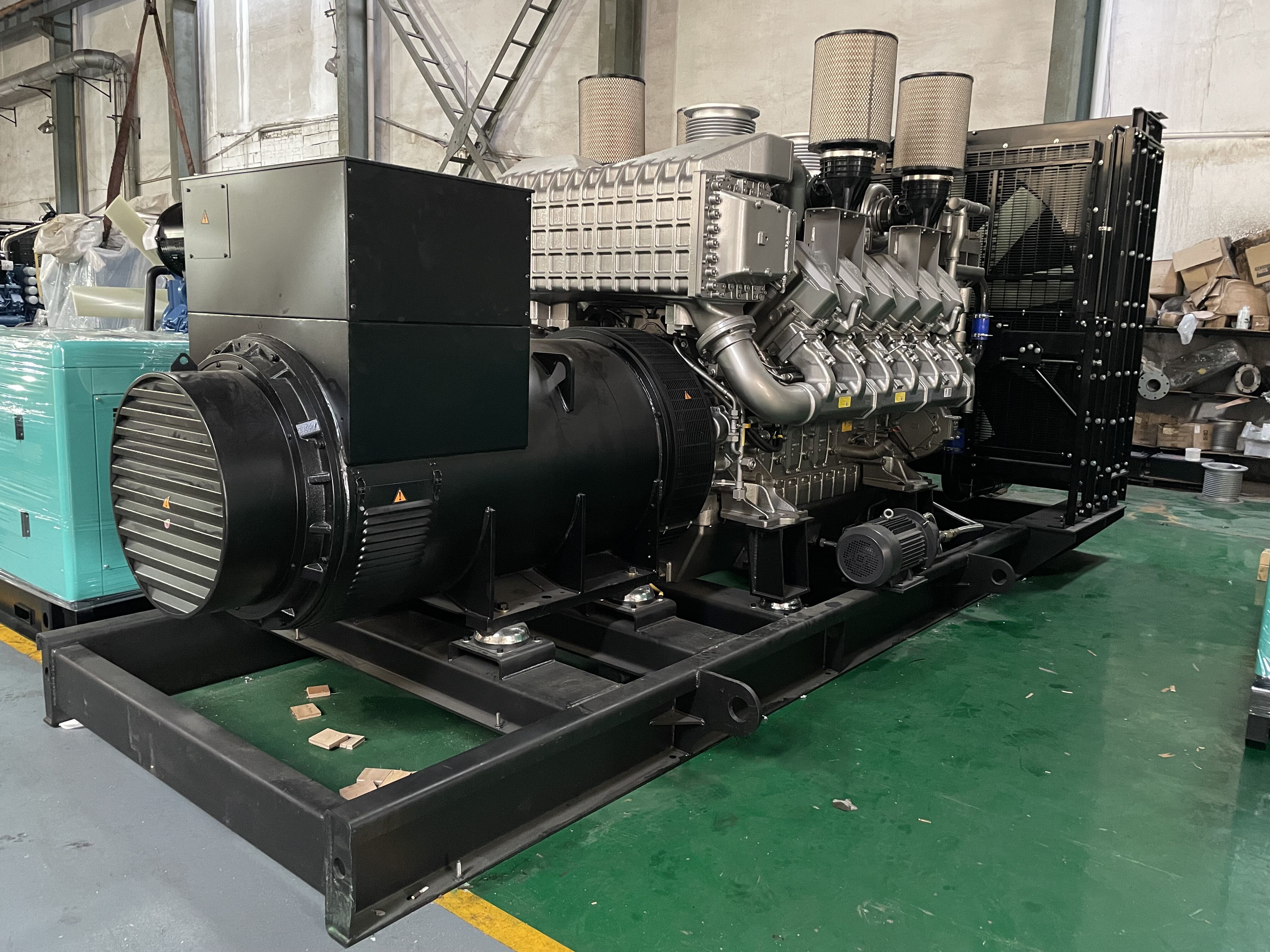
distributed power generation
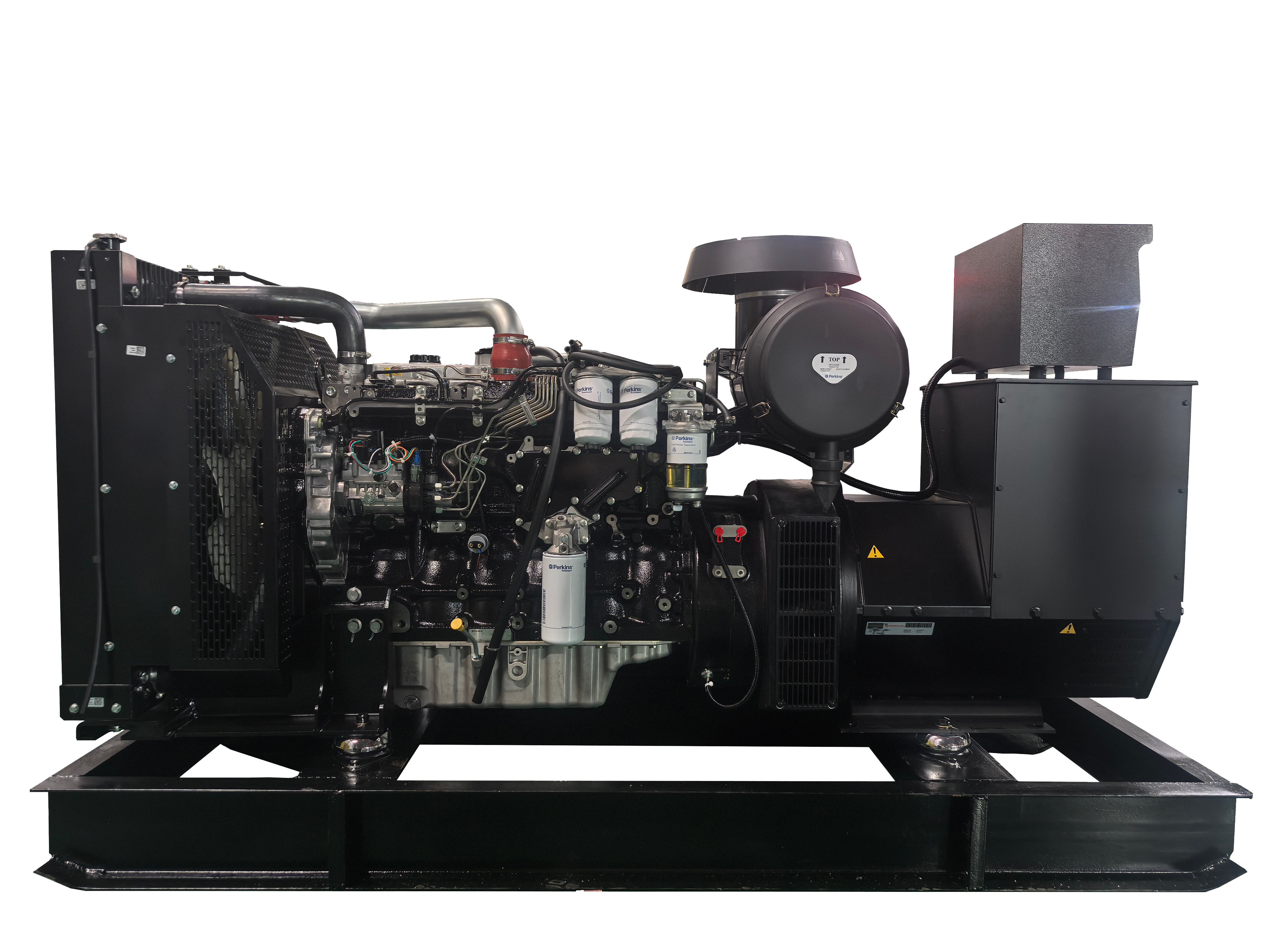
Distributed power generation represents a revolutionary approach to electricity production, where power is generated close to the point of consumption rather than at centralized facilities. This system encompasses various technologies including solar panels, wind turbines, microturbines, fuel cells, and combined heat and power systems. The fundamental principle involves generating electricity on a smaller scale, typically ranging from a few kilowatts to several megawatts, directly at or near consumer locations. These systems can operate independently or in conjunction with the main power grid, providing enhanced reliability and flexibility. The technology incorporates advanced control systems, power electronics, and smart grid capabilities, enabling real-time monitoring and optimization of power generation and consumption. Applications span across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors, serving diverse needs from powering individual homes to supporting manufacturing facilities. The systems often integrate energy storage solutions, allowing for better management of power supply and demand fluctuations. This decentralized approach to power generation has gained significant traction due to its ability to reduce transmission losses, increase energy efficiency, and provide greater energy independence.