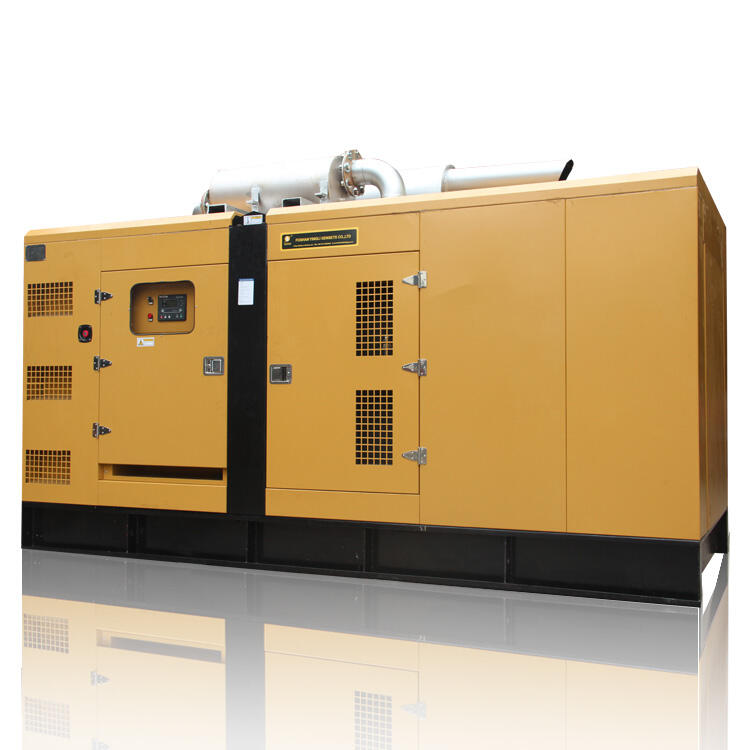
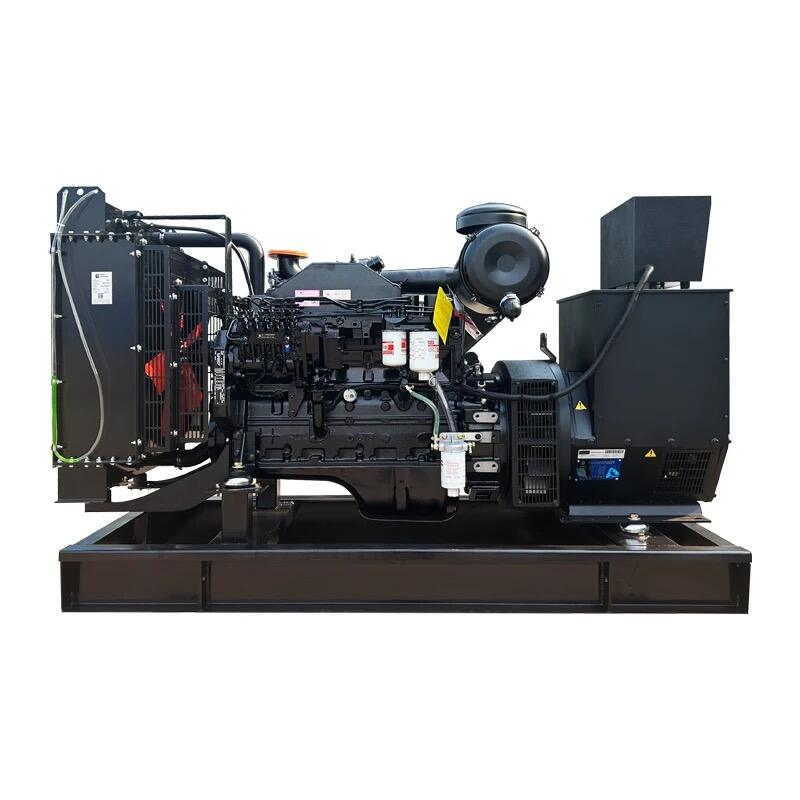
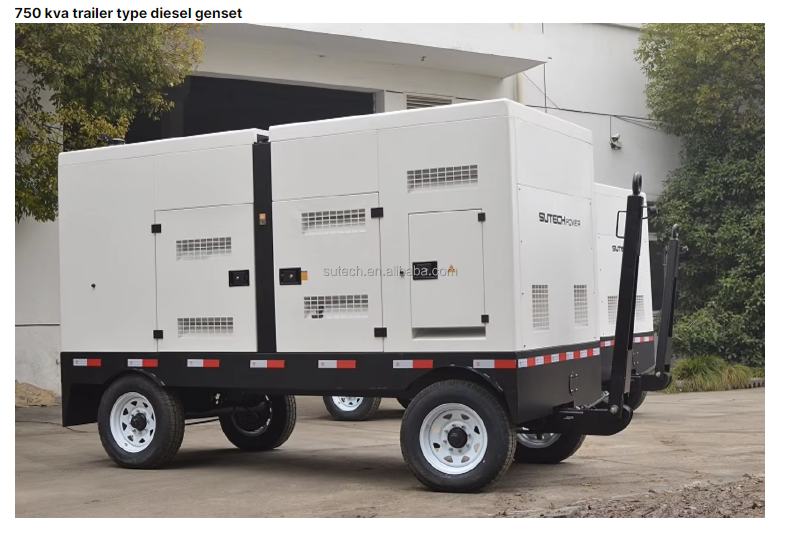
national grid power generation
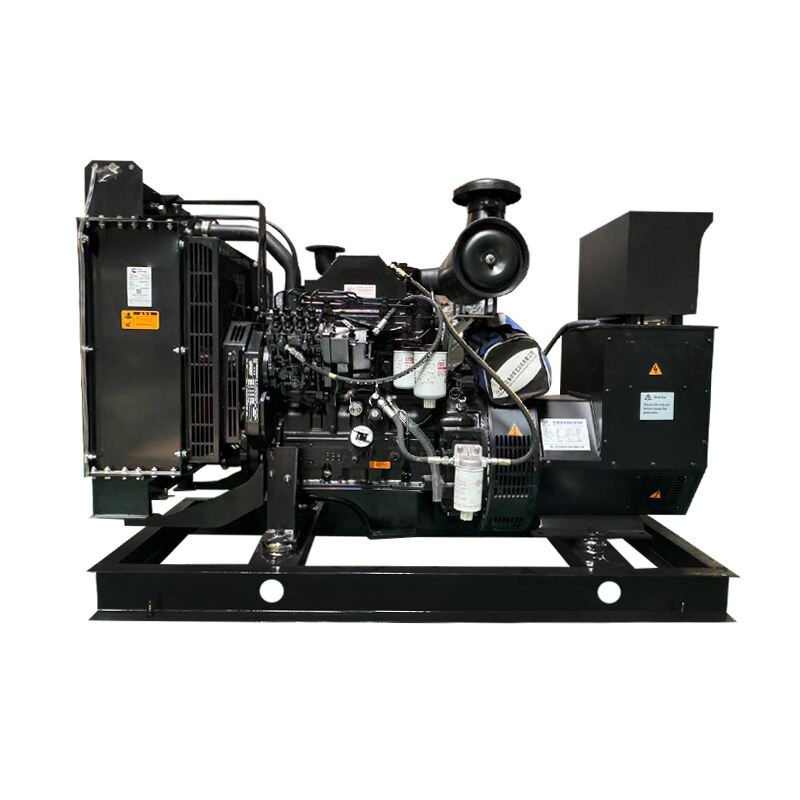
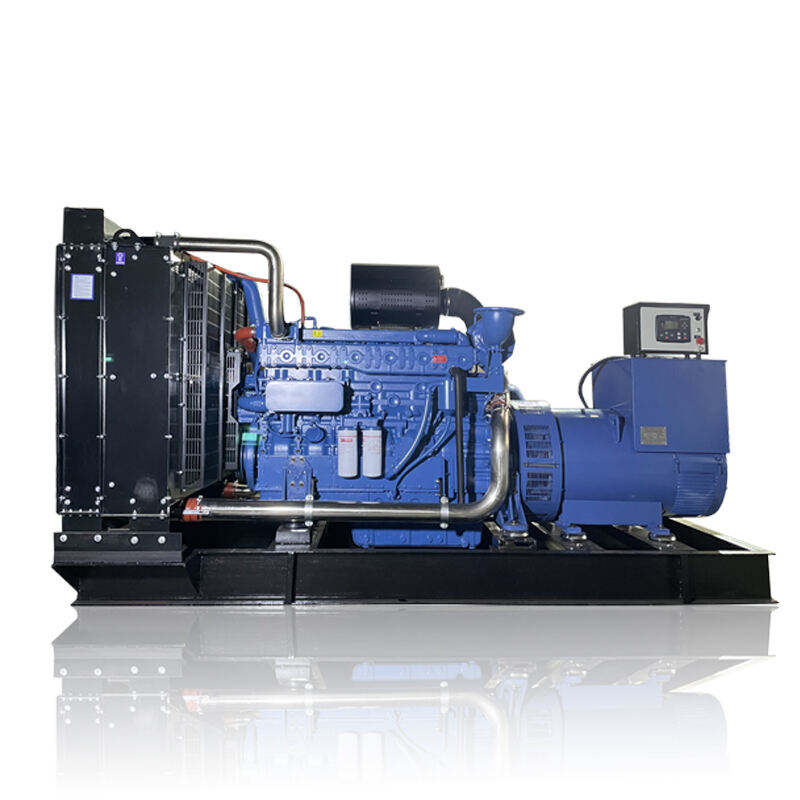
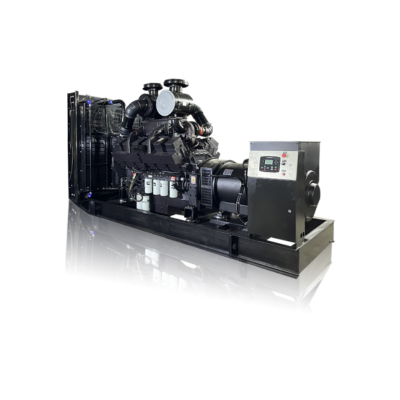
The national grid power generation system represents the backbone of modern electricity infrastructure, serving as a vast interconnected network that generates, transmits, and distributes electrical power across entire nations. This sophisticated system integrates various power generation sources, including thermal, nuclear, hydroelectric, and renewable energy facilities, working in perfect synchronization to ensure consistent power supply. The system employs advanced monitoring and control technologies, utilizing SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems to manage power flow and maintain grid stability. The generation process begins at power plants where electricity is produced at high voltages, typically 11kV to 33kV, before being stepped up through transformers for long-distance transmission at voltages ranging from 132kV to 400kV. The network incorporates redundant pathways and automated switching systems to prevent widespread outages and ensure reliability. Modern smart grid technologies enhance the system's efficiency through real-time load management and predictive maintenance capabilities, while also facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources. This comprehensive infrastructure supports industrial operations, commercial activities, and residential power needs while maintaining strict frequency and voltage parameters to protect connected equipment and ensure system stability.